Effective Arthritis Treatment: The Arthritis Disease Process

Federal reports show that the number of Americans suffering from arthritis is on the rise. The leading cause of disability in America, arthritis, costs the country $65 billion annually in lost productivity and medical care. According to the CDC (Centers for Disease Control), arthritis has increased in number by 750,000 per year since 1990. Worse, the CDC predicts that the US will have 60 million people with the disease by 2020, compared to 43 million in 1997. More than 11 million people will be affected by the condition out of 60 million.
Understanding Arthritis Treatment is Key to Success
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. About 70% of those over 40 have at minimum x-ray evidence. Osteoarthritis usually affects two types of joints: those that support weight (e.g. the lower back, hips and knees) and those that perform repetitive motions (e.g. the hands, wrists and shoulders). Osteoarthritis may also occur in injured joints such as the vertebrae in the neck following a whiplash injury, or the knees of football players.
Arthritis Treatment: The Role of Cartilage
Osteoarthritis, which is also known as osteoarthritis, is a disease that affects the cartilage and not the bone. Degenerative joint disease, or DJD, is the most recent name for osteoarthritis.
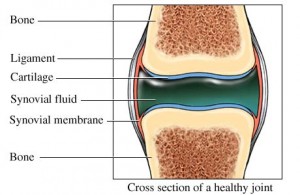
Anatomy of a Joint
A joint is composed of two bones that are connected by a capsule made of ligaments. A thin layer of cartilage is found at the ends of each bone. This cartilage layer acts like a cushion between bones and absorbs the strain on joints when they move.
Collagen - Strong but not indestructible
Even though cartilage is strong, it is susceptible to damage from injury. Cartilage is composed of collagen protein strands that form a strong, mesh-like framework. Proteoglycans are substances that hold water and act like sponges. Water is sucked out of the mesh when weight is added to cartilage. The water will return to the mesh if weight is removed.
It is hard to heal cartilage
Because cartilage doesn't contain blood vessels, it makes it more difficult to heal injuries. It does not have nerves. This means problems can go undiagnosed until there is significant degeneration.
Chrondrocytes are the Key to a Delicate Balance
The normal balance between building up and wearing down cartilage cells (called "chondrocytes") is similar to that of our skin. This delicate balance is vital for the health and well-being of our joints.
The Osteoarthritis Epidemic
Understanding the cartilage balance of our joints is key to understanding the costly mistakes in medical treatment for osteoarthritis. Here's why. Osteoarthritis causes cartilage to wear down more quickly than it can be rebuilt, and it does so gradually. It is reasonable to conclude that any activity that encourages the growth of cartilage cells will be beneficial to the joint. Conversely, anything that promotes their destruction would be detrimental to the joint. Now you have the knowledge to understand the Osteoarthritis Epidemic.
Are prescription and over-the-counter drugs contributing to osteoarthritis progression? I'll let you decide. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, also known as NSAIDs, are the most common treatment for osteoarthritis. OTCs, also known as ibuprofen or aspirin, are used to treat osteoarthritis.
Arthritis Treatment: NSAIDs Have Potential Side Effects
Side effects of NSAIDs include stomach irritation, ulcers, and increased blood pressure. However, there are also some less well-known side effect like swelling and increased blood pressure. There is also the possibility for liver and kidney damage. Your doctor may request periodic blood tests to determine if there is any liver damage.
Safety of Arthritis Treatment Drugs Question
Even though the results are not conclusive, a new study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association shows that NSAIDs could actually increase your risk of having a heart attack.
Valentin Fuster MD, former president of American Heart Association, made this statement:
"Even though the study is not perfect, the findings cannot be thrown into the wastebasket." He warned, "Because so many people use the drugs - more than 2 million prescriptions will be written this year - we had better pay attention to this observation".